Electronics load
1. Overview of Electronic Load and Its Role in DC Power Supply Testing
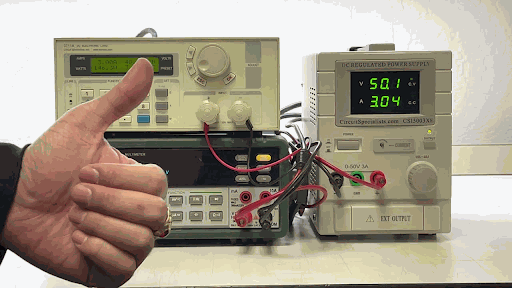
1.1 What is an electronic load?
An electronic load is a specialized testing device used to simulate electrical loads on DC power supplies to evaluate their performance. Instead of using traditional resistive loads, an electronic load allows flexible adjustment of operating modes such as Constant Current (CC), Constant Voltage (CV), Constant Power (CP), and Constant Resistance (CR), enabling accurate simulation of various load conditions.
1.2 What is its role in DC power supply testing?
Using an electronic load in DC power supply testing provides several benefits:
Direct and accurate measurement of energy conversion efficiency.
Testing of load capacity, overcurrent protection, voltage stability, and other characteristics of the power supply.
Detection of thermal and electromagnetic interference issues during operation.
Electronic loads are widely used in industries such as power supply manufacturing, mobile devices, batteries, solar energy, and UPS systems.
2. DC Power Supply Testing Process Using Electronic Load and Sterilization of Electronic Load
2.1 Operating Modes of Electronic Load
An electronic load can operate in four main modes:
Constant Current (CC) Mode: The load maintains a stable current regardless of changes in input voltage. Suitable for testing power supplies and measuring power consumption.
Constant Voltage (CV) Mode: The load adjusts current to keep the input voltage constant, commonly used for testing battery chargers.
Constant Power (CP) Mode: The load adjusts both current and voltage to maintain a constant power draw, useful for evaluating a power supply’s power delivery capability.
Constant Resistance (CR) Mode: The electronic load behaves as a pure resistor, where current is proportional to voltage, ideal for testing startup behavior and current limiting features of the supply.
Choosing the appropriate mode enables accurate assessment of the DC power supply’s technical characteristics under various real-world conditions.
2.2 DC Power Supply Testing Process
The typical process for testing a DC power supply using an electronic load includes the following steps:
Connect the electronic load to the DC power supply under test.
Select the appropriate operating mode (CC, CV, CP, CR).
Adjust the load according to the test requirements, e.g., gradually increase the load current to evaluate maximum load capacity.
Measure and record parameters such as voltage, current, power, temperature, and other indicators.
Analyze the data to assess performance, stability, and protection features of the power supply.
2.3 Sterilization of Electronic Load
In environments where electronic devices are manufactured or tested—especially in high-cleanliness sectors like medical or semiconductor industries—sterilizing the electronic load is crucial to avoid contamination or test result distortion.
Sterilizing the electronic load helps remove dust, bacteria, and impurities that could affect accuracy and durability of the device.
Common sterilization methods include using ozone gas, UV light, or suitable disinfectant solutions compatible with the load’s materials.
Sterilization should be performed regularly, especially after each testing cycle or when the device is used in special environments.
Maintaining a clean electronic load not only protects the equipment but also ensures DC power supply test results remain accurate and reliable.
3. Benefits of Using Electronic Load in DC Power Supply Testing

High Accuracy: Electronic loads allow precise adjustment of load parameters, enabling simulation of realistic operating conditions for DC power supplies.
Time and Cost Efficiency: Compared to traditional load testing methods, electronic loads reduce testing time and lower maintenance costs, as there's no need to change physical resistors.
Wide Range of Applications: Suitable for testing various power sources such as batteries, chargers, industrial power supplies, UPS systems, and solar energy systems.
Improved Durability and Lifespan of Equipment: Thorough testing helps detect issues early, allowing timely intervention and enhancing the longevity of power supplies.
Easy Integration and Automation: Many modern electronic loads support programming and computer connectivity, enabling automated testing and data acquisition.
Types of Electronics load (2,094)
- AC/DC electronic load (133)
- DC electronic load (1,735)
- LED DC Electronic Load Simulator (24)
- Mainframe (7)
- Power Supply Tester (2)
- Regenerative DC electronic load (193)
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
