Prodigit develops the latest 3310G Series electronic loads.
The 3310G is a highly upgraded version of the successful 3310G series electronic load family.
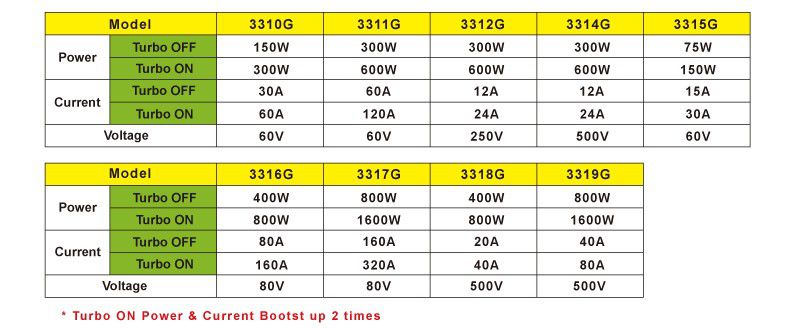
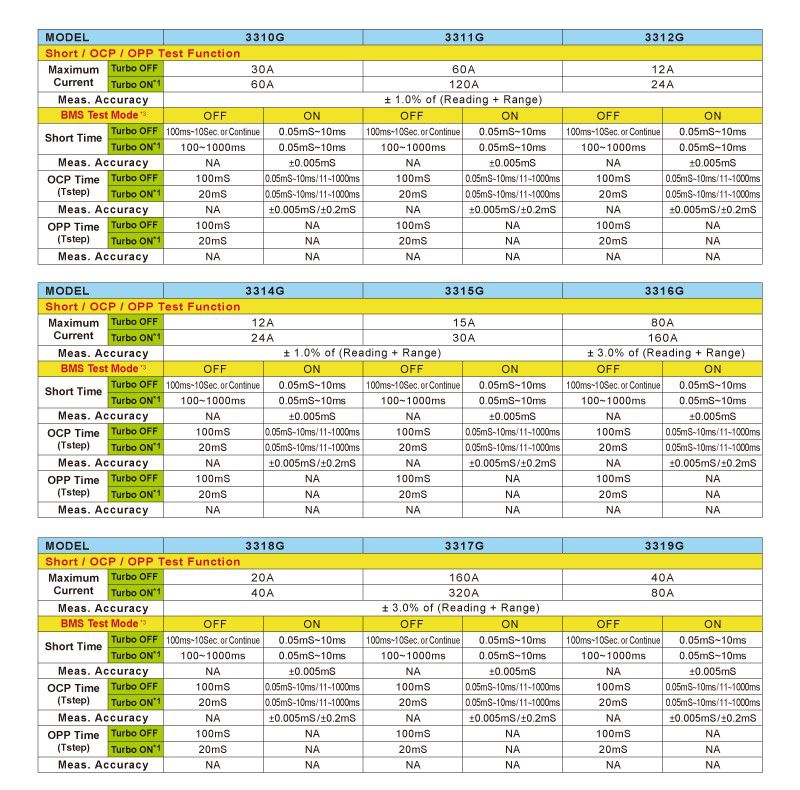
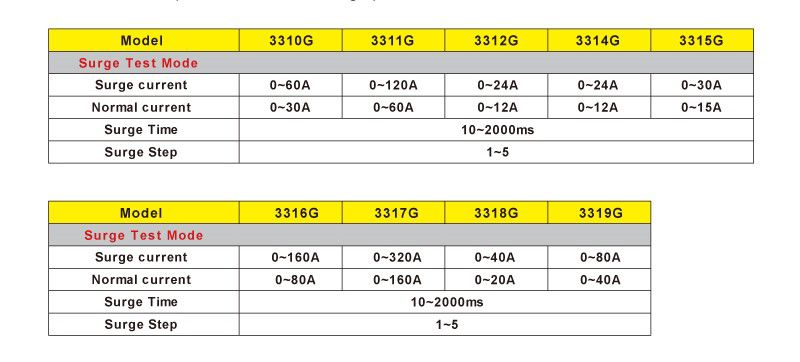
The 3310G Series consist of the following models:
- 3310G (60V/ 30A, 150W)
- 3311G (60V/ 60A, 300W)
- 3312G (250V/ 12A, 300W)
- 3314G (500V/ 12A, 300W)
- 3315G (60V / 15A, 75W)
- 3316G (80V / 80A, 100W)
- 3317G (80V / 160A, 800W)
- 3318G (500V / 20A, 400W)
- 3319G (500V / 40A, 800W)
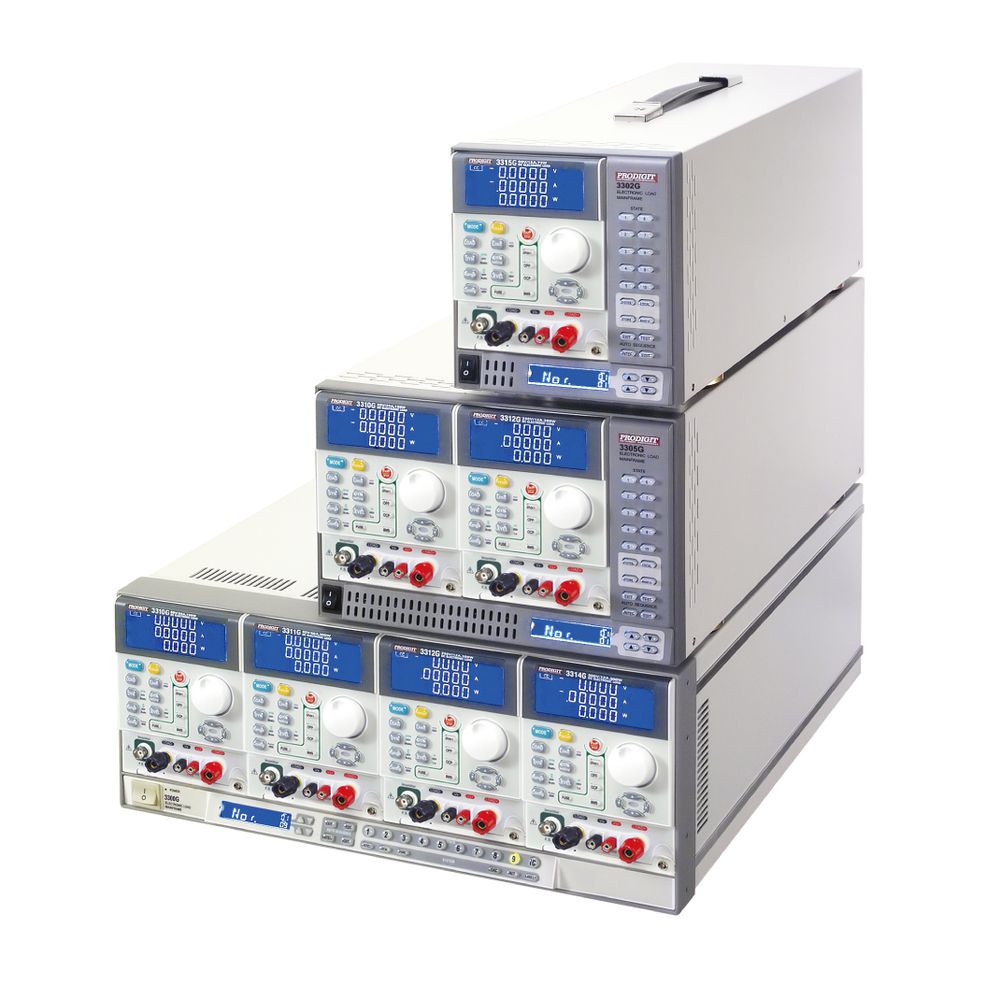

The model table below highlights the different power and current capabilities for each model.
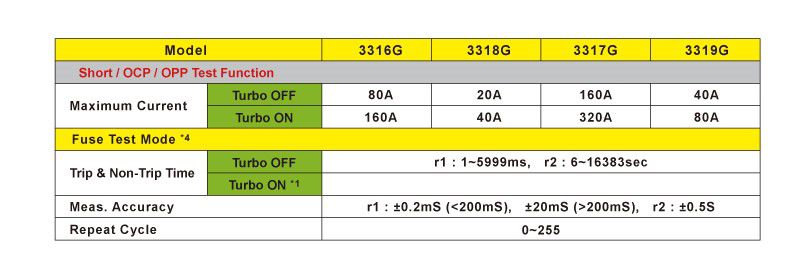
Model list of 3310G Series Electronic Load with Turbo mode.
The 3310G series electronic load module can be used with the 3300G series mainframe, including single-3302G mainframe, dual 3305G mainframe and 4-channel 3300G mainframe. The 3317G/3319G is a stand-alone electronic load.
In addition to carrying over the outstanding performance of the 3310F series, the 3310G Series electronic Loads add a unique Turbo mode. This mode allows the load to support up to two times the rated current and power of a 3310F Series load for short periods of time.Turbo mode is very valuable for enhanced protection testing of power products. Examples include power supplies, Battery Management Systems (BMS) and protection devices such as Fuses / Breakers or PTC Resettable fuses. In doing so, the 3310G Series can test and verify the actual trip current levels and response times under abnormal operating conditions.
The current can be increased by 2 times during the test which can improve the test current shortage of electronic load.
The built-in test functions for Turbo mode include Short, OCP, OPP, BMS and Fuse tests.

The following example illustrates the ease of performing these kinds of tests with the 3310G Loads.
1. Turbo mode ON/OFF indicator, Turbo mode includes Short, OCP, OPP, BMS, Fuse test functions, the other new functions are MPPT with CC and CR mode, CV response time setting, Battery discharge Batt1 ~ Batt3 in Config key.
2. Fuse (Current Protection Components) Test function key.
3. BMS (Battery Management System) test mode key.
4. Add CC+CV and CP+CV for battery discharge test.
In addition to the Turbo mode, the new loads also support NTC resistor simulation, which is an option on the 3310F/G series / 3302F/G mainframe. These load functions support a wide range of battery discharge testing. Particularly useful for these applications are the new CC + CV and CP + CV operation modes, battery discharge capacity test and dynamic cycle discharge test. Each of these new features is described in detail in the following paragraphs:
1. Overload Protection Testing of power suppliesThis applies to AC/DC, DC/DC Power Supplies, DC/AC inverters, Power Adapters and Device Chargers. These products are not only designed to supply a stable voltage or current, they also need to protect load against abnormal conditions in order to ensure safe operation under all conditions. They are to prevent overheating or high temperature due to excessive current, which could result in a fire and other hazards.
Short circuit, Over Current and Over Power are all abnormal conditions. These conditions typically represent 125% to 150% of the normal rating and in some cases even more. Therefore, to simulate these abnormal conditions, the maximum current value and the maximum power value of the electronic load to perform these tests must be up to two times the normal rating. One solution is to use a load that is twice as big as needed for normal testing but this will cost more. A better alternative is to use the 3310G Series loads, which can provide up to four times rated power and current conditions with a normal rated model.
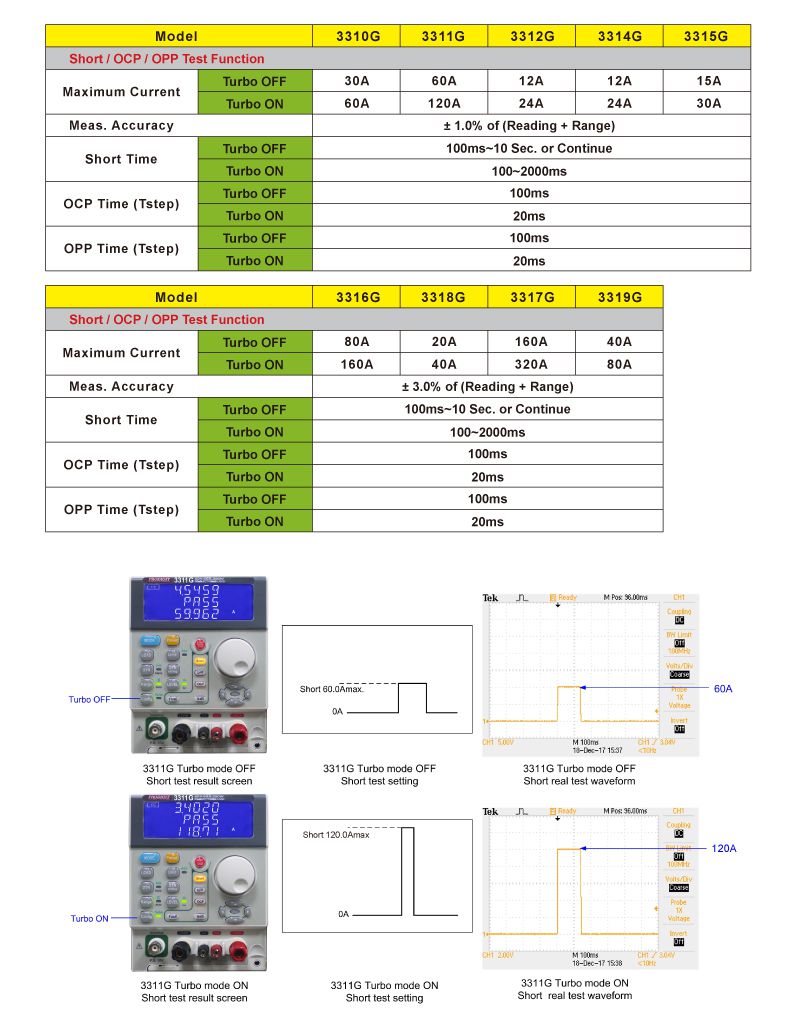
The power supply products under test must respond with the appropriate protection function but the abnormal situation duration is often quite short. To test for conditions, Prodigit's 3310G Series electronic load can increase the electronic load current and power in the new Turbo mode some period of time (within 2 seconds) up to 2 times the rated value. For example, the 3311G 60V /60A/ 300W in Turbo mode can increase its load current to 120A or power to 600W electronic load for up to two seconds. When verifying power products using Turbo mode in a production test environment, 3310G Series electronic loads offer greater test verification capability compared to conventional DC loads. Furthermore, the 3310G Series built-in measurement circuits can also measure the actual trip current value and protection response time under short-circuit or overload test conditions.
2. BMS Protective DevicesLithium batteries are widely used in a variety of electronic products and electric vehicles and other devices. In order to protect the lithium battery from catching fire, exploding or any other dangerous condition, the lithium battery must be designed with a Battery Management System (BMS) protection circuit. The BMS ensures the charging voltage does not exceed the maximum safe value of the lithium battery (Over Voltage Protection or OVP) during charge cycles. It also monitors discharge to ensure the battery does short-circuit or exceed its rated current (Over Current Protection or OCP). Finally, internal battery and cell temperatures are monitored for over or under temperature protection (OTP/UTP).
Previous Prodigit 3310F Series electronic loads were developed with BMS test functions back in 2015 as an option on the 3302F mainframe. The 3310G Series electronic now includes standard BMS test functions. Furthermore, the new Turbo mode allows the short circuit protection current and overcurrent protection to be 2 times larger depending on the 3310G model.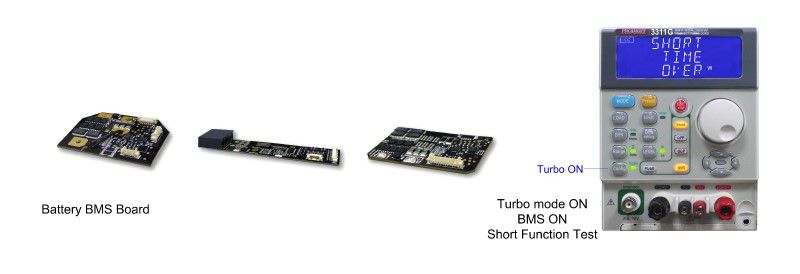
The 3310G Series BMS test function for lithium batteries includes short circuit and overcurrent protection modes, which provide a quick, easy and accurate test solution. For BMS short-circuit protection, there is about four times more current available for OCP current testing that needs immediate (uS level) protection action function, use 3311G up to 120A current load, in the process of high current pull to BMS rated short circuit current, it can verify BMS short circuit protection can do correct action.
In addition, the 3310G series electronic load can also detect the actual operating current value and operating time of the BMS short circuit protection action, that is, the actual operating current value and operating time when the BMS internal MOSFET switch is turned off.
For BMS overcurrent protection, it is between normal operating current and short-circuit current protection, generally higher than 125% of OCP current, it needs fast (about several hundred mS level) protection action.
3310G series BMS overcurrent (overcurrent during charging and overcurrent during discharge) protection test system with electronic load pull, then confirm whether BMS overcurrent protection is active, when BMS overcurrent protection is not active, increase load current (I Step). Then, confirm whether the OCP of the BMS is active, and continue the process until the BMS OCP action occurs. Therefore, the BMS OCP test can be scanned by gradually increasing the load current to obtain the current point and action reaction time of the BMS overcurrent protection.
2.1 BMS short circuit, overcharge current, over discharge current protection principle.The BMS circuit protection principle is as shown in the figure below. It is to protect the battery by turning off the MOSFET (loop current = 0A).
In the BMS, the MOSFET switch is bidirectional. In the normal status, the two switches are ON. Since the two MOSFET switches have the Rds ON resistance, current flow will cause a voltage drop. Battery BMS uses this feature to detect charge and discharge currents.
The MOSFET switching status shown in the figure below is the over-discharge current status. The IC's 3rd pin control MOSFET is ON, this time the discharge switch is OFF (controlled by IC pin 1).
When the BMS detects a short circuit, over discharge current or low battery voltage, it will turn off the discharge switch to protect the battery.
When the BMS detects an overcharge current or a battery overvoltage, it will turn off the charge switch to protect the battery.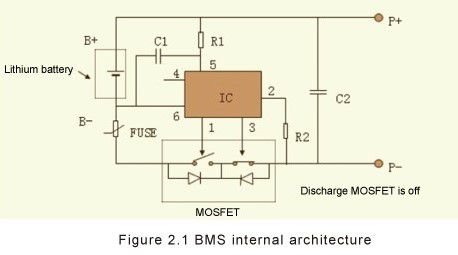
2.2 Short-circuit protection (SHORT) test method:
Power supply (PS) & LOAD connection is shown in Figure 2.1, LOAD test procedure is shown in Figure 2.3.
In the short-circuit protection test mode, the electronic load will load the maximum current value of the model (for example, 60A for 3311G or 120A for Turbo ON). At the same time, the timer is started to calculate the actual time flowing through the BMS (Note: This time refers to the time between the set threshold current Ith to the BMS action MOSFET switch OFF, that is, the time lower than the set threshold current Ith.
In addition, the electronic load will measure the actual maximum short circuit current value, Figure 2.4 is 4000 mAh mobile power uses the 3311G BMS test oscilloscope current waveform (left figure) and the electronic load power meter to show the short circuit maximum actual current and short circuit protection reaction time (right figure).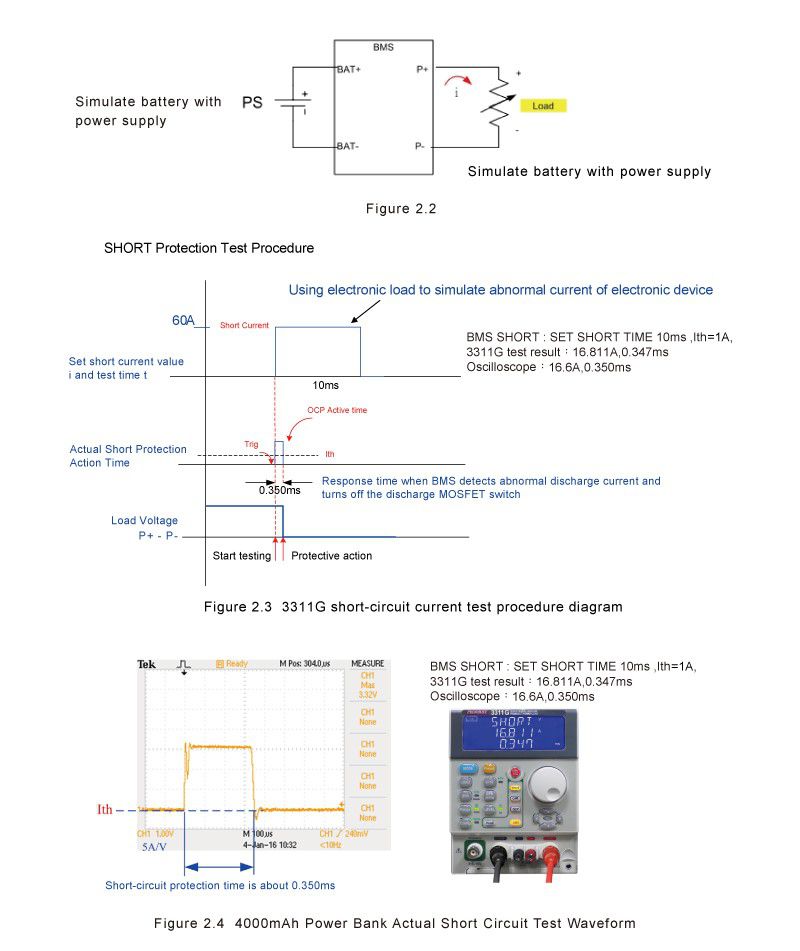
2.3 Overcharge Current Protection (OCCP) test method:
The test method is divided into single pulse and continuous step pulse. Single pulse can be used for rapid tests. It can be used for a large number of fast tests suitable for the production line. Continuous step pulse can be used to scan the actual over current protection point. Suitable for research and development that needs accurate point. The power supply (PS) & LOAD connection and test procedures are shown in Figure 2.5.
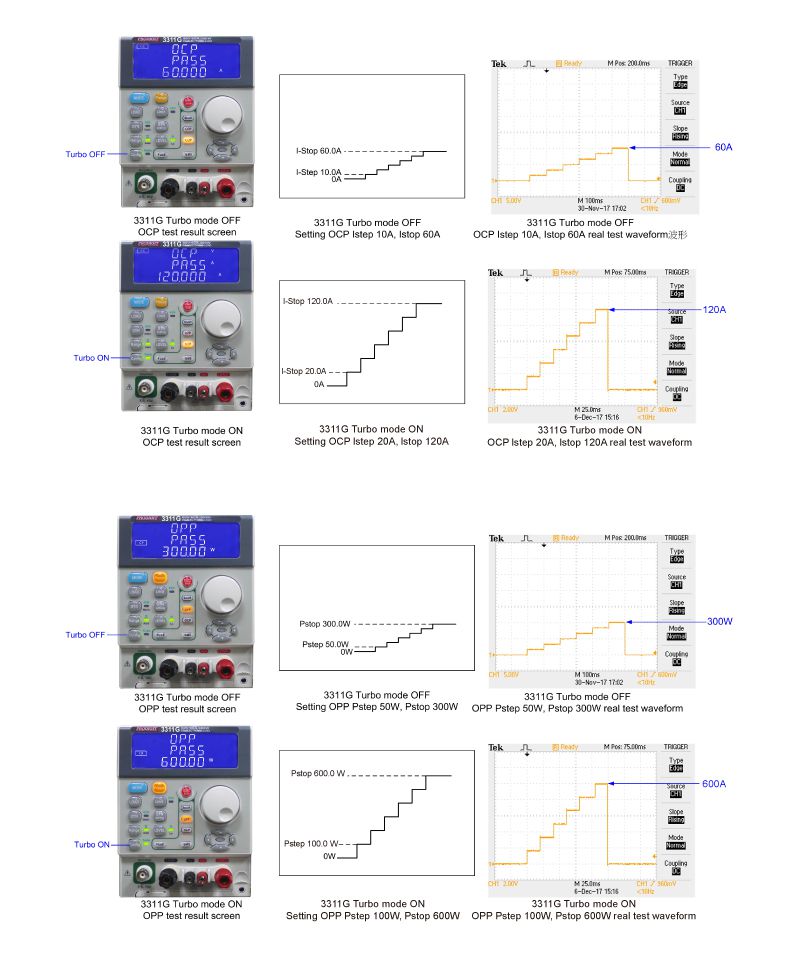
2.2.1. In the single-pulse overcurrent protection test mode, the electronic load will be pulled to the set current value (for example, 3311G is the current value between 0~60A or 120A when Turbo is ON), at this time, the electronic load measures the actual maximum overcurrent protection value and the overcurrent response time value. Figure 2.6 is the 3311G single pulse current BMS overcharge current test program diagram. Figure 2.7 is the actual test result, the left picture is the oscilloscope current waveform when BMS overcharge current protection. The figure on the right shows the actual test overcharge current value and protection reaction time of the 3311G BMS.
2.2.2 The overcurrent protection test mode of continuous STEP pulse is similar to the single pulse mode. In addition to the initial current setting, the continuous STEP pulse mode increases the time of each STEP, the current increased by each STEP and the current value of the final STEP. Figure 2.8 is the 3311G single pulse current BMS overcharge current test program diagram. Figure 2.9 is the actual test result, the left picture is the oscilloscope current waveform diagram when BMS overcharge current protection, the right picture is the actual test overcharge current value of 3311G BMS and Protect the reaction time.
2.2.3 In continuous STEP pulse mode, the maximum overcurrent protection value and overcurrent action reaction time value measured by the electronic load are the measurement results under each STEP. For example, if ISTART is set to 1.000A, OCT TSTEP is 500ms, OCP ISTEP is 0.1A, OCP ISTOP is 5.000A, the measurement process is the electronic load sink current 1.000A and test whether the battery BMS operates at 500ms. If it is, it will measure the action current value and the action reaction time. If the battery BMS is no action under 1.000A, the electronic load will increase to 1.100A according to ISTEP setting, and test whether it operates at 500ms. If it is, it will measure the operating voltage value and action time at 1.100A. If the battery BMS is no action at 1.100A. the load current is increased to 1.200A in the above manner until the final test voltage value of the battery BMS test is 5.000A.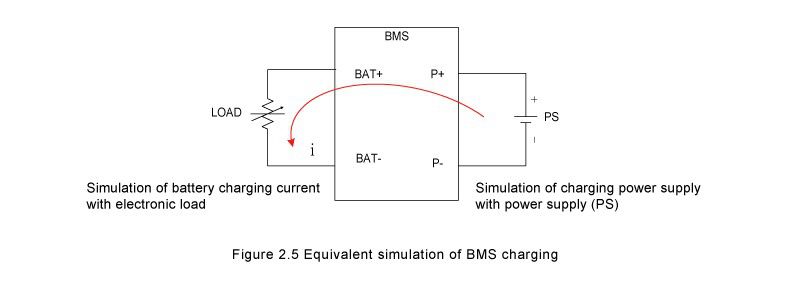
2.2.4 Continuous Step Pulse: Use when scanning the actual overcurrent protection point during charging OCCP (Over Current Charge Protection) Test Procedure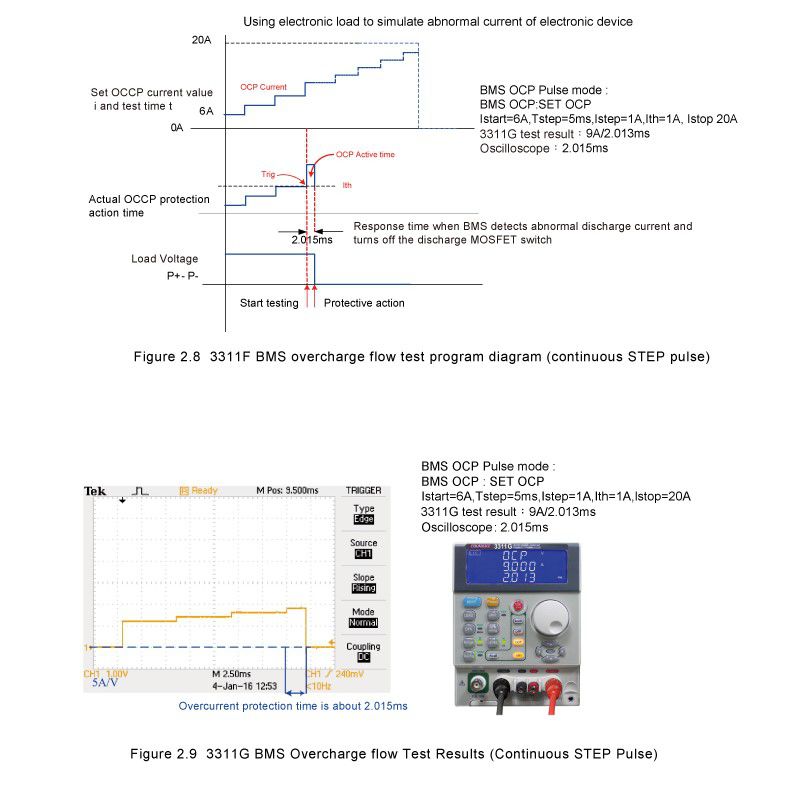
2.4 Overcurrent discharge protection (OCDP) test method: Power supply (PS) & LOAD connection and test procedures are shown in Figure 2.10.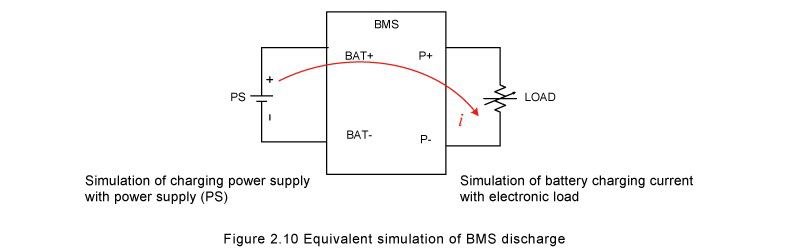
2.4.1 Single Pulse: Used during quick test.
OCDP(Over Current Discharge Protection) Test Procedure.
The 3311G single pulse current BMS overdischarge current test procedure is similar to the BMS overcharge current test. The 3311G BMS function can actually test the overcharge current value and the protection reaction time.
2.4.2 Continuous Step Pulse: Used when the actual overcurrent protection point during scan discharge.
OCDP (Over Current Discharge Protection) Test Procedure.
The 3311G continuous pulse current BMS overdischarge current test procedure is similar to the BMS overcharge current test. The 3311G BMS function can actually test the overcharge current value and reaction time.
2.5 The function and actual action response of the battery BMS have been explained in detail.
The battery BMS can immediately provide protection and disconnection measures for the abnormal voltage, current, temperature and other conditions of the battery to avoid the occurrence of danger; because the battery BMS is a safety measure that must be 100% full-featured test verification that security can be ensured. Although the test and verification for the battery BMS can use the oscilloscope to measure the current value and action response time of the BMS action, it is undoubted that the oscilloscope can be tested in detail during the development stage. But in a mass production stage, there is a need for rapid and complete testing and there is a limit on capacity production. For this difficulty, Prodigit integrates the BMS test into the 3310G series electronic load. In addition to the functions of the normal 3310G series, the set test current required for battery BMS testing is increased. Both the current action value and the action response timer are integrated into the 3311G BMS function, allowing a large number of quick tests to verify that the battery BMS becomes a reliable, accurate and fast method.
To test BMS over-current protection, the 3310G load starts to sink current (I start), then checks whether the BMS over-current protection is active. If the BMS over-current protection is not active, the load starts to increase the load current (I Step) and checks whether the BMS OCP responds. This process continues until the BMS OCP activates. Thus, the BMS OCP test can determine both OCP function current trip level and response time.
3. Current protection for component testing
Common current protection devices include Fuses, Breakers and newer PTC Resettable fuses etc. Their role is to disconnect a load when the actual current exceeds the rated current of the load to avoid overheating, even fire, and other dangerous conditions. Therefore, the current protection component is the last line of defense to ensure safety when the load current is abnormal. When an abnormality occurs, the protective device must be able to provide the protection capability for disconnecting the circuit. The protection of these components have their own function and different price points. For example, a fuse is a one-time use device while circuit breakers and PTCs are reusable.
The current rating of the current protection component usually has a product relationship with the protection response time. The greater the current through the current protection component, the faster the reaction time. That means it is related to the total energy into the protection component.
To test these protection devices, the 3310G Series of electronic loads are specifically designed for test verification of current protection components. A Fuse Test function that can be used with Turbo mode that provides 2 times the rated current and power for a short period of time. This allows testing and verification of these components with about 2 times the current and power specifications of the components.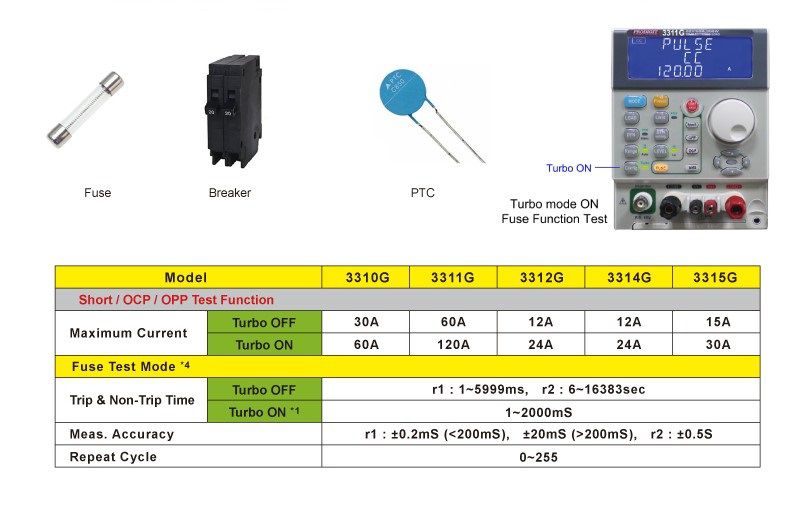
Fuse Test functions are divided into two types, Trip (fuse) and Non-Trip (no fuse).
Fuse Test setting parameters include the test current (Pulse CC), the test time (PULSE TIME), the number of test repetitions (PULSE REPEAT) Cycles and the Ith or current threshold value.
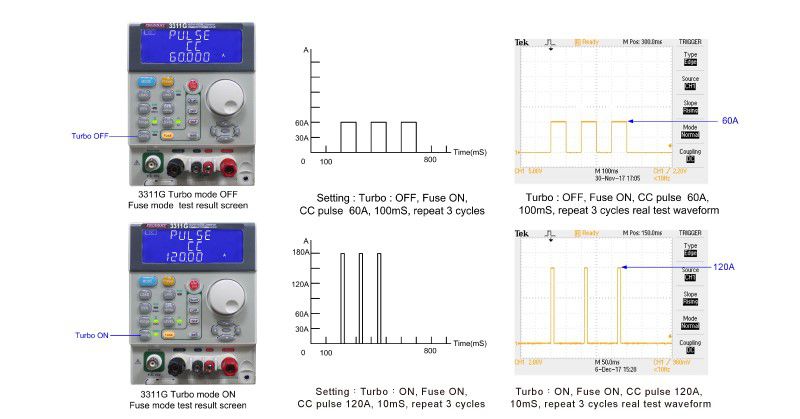
The fuse Trip test determines that when the current is too large the device can provide the protection of an open circuit. This means the current protection components need to have a fuse action. To test this, the test current needs to be greater than the fuse current specification. After the fuse blows or Circuit Breaker trips, the 3310G Series electronic load determines if the current is lower than the programmed Ith current threshold value. The load LCD will display the Repeat Cycle and the fusing time in ms.For the Non-Trip test, the current protection component is required to achieve non-blown action, so the test current needs to be lower than the fuse current specification. To verify that at normal current levels the device does not trip, the 3310G Series electronic load checks that during the test time (Pulse Time) the device does not trip after repeating the number of repeat cycles. The load LCD will display the number of Repeat Cycles applied.
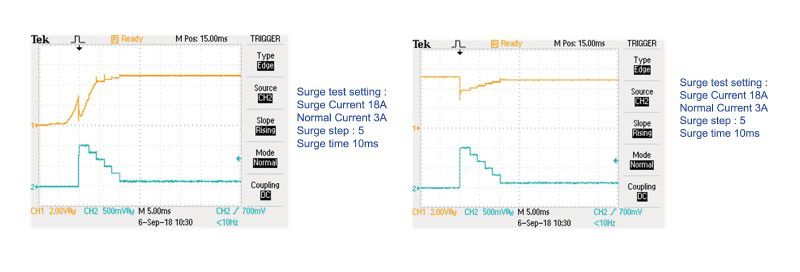
4. The capacitive load and sudden hot Plug-in test of power supply at startupThe power input circuit of the electronic circuit usually has many high-capacity capacitors, so the output of the power supply will have an instantaneous starting current when the power is turned on. The 3310G series has a unique surge current test mode, which can provide instantly up to 200% load specification current (example: 3311G continuous current specification 60A and maximum surge current can be tested to 120A) Test time up to 2000 ms, can be used to power the power supply or charger connected to the electronic circuit at boot. The instantaneous starting current of the simulated load is used to test whether the output voltage waveform of the capacitive load meets the requirements when starting up, as shown below.
In addition, when the power supply or charger is in operation, the hot plug-in electrical equipment will cause a surge load current when it is connected. The 3311G series incorporates the running surge current test function to view the electrical appliances when the load is suddenly connected, to see if the power supply or charger output voltage is stable enough. As shown below.
 5. NTC simulation test (this feature is optional)
5. NTC simulation test (this feature is optional)Based on the safety issues with lithium batteries and the effect of ambient temperature, lithium batteries and chargers must require a temperature protection mechanism to prevent causing danger under ambient low and high temperature conditions.

The 3310G Series electronic loads and 3302G mainframe support the NTC resistor simulator option. The 3310G Series can set NTC resistor values from 1000 to 500KΩ, equivalent to 10KQ NTC resistance for a temperature range from -46°C to +179°C. Changing the NTC resistance verifies if the lithium battery and charger temperature protection system operate correctly by either halting the charge or discharge cycle or by reducing the charge and discharge current. When the temperature returns to normal working temperature levels, the load checks if the protection action recovers and returns to the operational state, i.e. restores the normal charge and discharge.
6. Load operation mode supports CC+CV and CP+CV modeThe 3310G Series electronic loads not only include 3310F Series functions like CC, CR, CV, CP, Dynamic load mode, it also adds the new CC + CV and CP + CV operation modes.
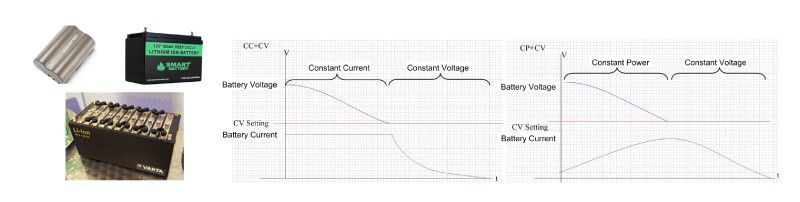
During discharge testing of batteries, special attention should be paid to avoid over-discharge. This will cause the battery voltage to drop too low and cause permanent damage.
When using the CC + CV or CP + CV mode of the 3310G Series electronic load, the battery will respond to constant current (CC) or constant power (CP) mode set by the electronic load to discharge. When the minimum allowable discharge voltage of the battery is set as the CV voltage value - the lowest voltage of the discharge test - the CC + CV and CP + CV modes can ensure the battery will not be damaged due to overdischarge, resulting in battery loss.
7. Battery test functionThe 3310G Series load also supports five new battery discharge tests, TYPE1 ~ TYPE5. You can select the appropriate battery test mode and test results can be directly displayed on the LCD display showing the battery AH capacity, the discharge voltage value, the cumulative discharge time data etc.
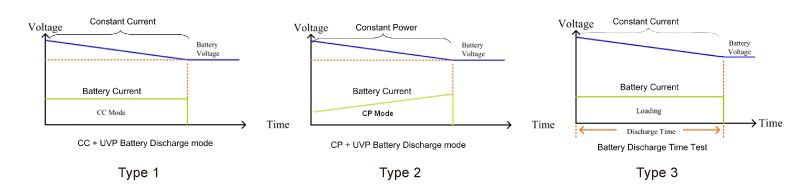
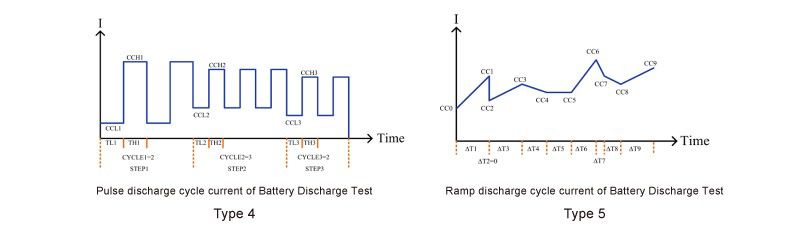
There are also CC pulse cycle life test and CC Ramp Cycle life test types (Type 4, Type5 provides remote operating only). These can be used to simulate the battery in actual use by using a variety of load current changes and cycle variations. The user can verify and simulate the performance and life during actual use of batteries.
 8. Battery real discharge current simulation and test
8. Battery real discharge current simulation and testThe 9923 Current Waveform Generator can be added as needed to provide battery real discharge current waveform simulation.
The new Model 9923 Current Waveform Generator (Option) provides real battery discharge current waveform simulation. This option installs in Model 9923 to 3302G, 3305G and 3300G Series load mainframes and can simulate real battery discharge current waveforms.
Please refer to the Model 9923 Current Waveform Generator application for details.























